40 changed files with 328 additions and 196 deletions
+ 4
- 0
docs/assets/styles/_markdown.scss
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 1
- 0
docs/assets/styles/_shortcodes.scss
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 2
- 7
docs/content/developer-guide/channels/index.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 1
- 1
docs/content/developer-guide/configuration.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
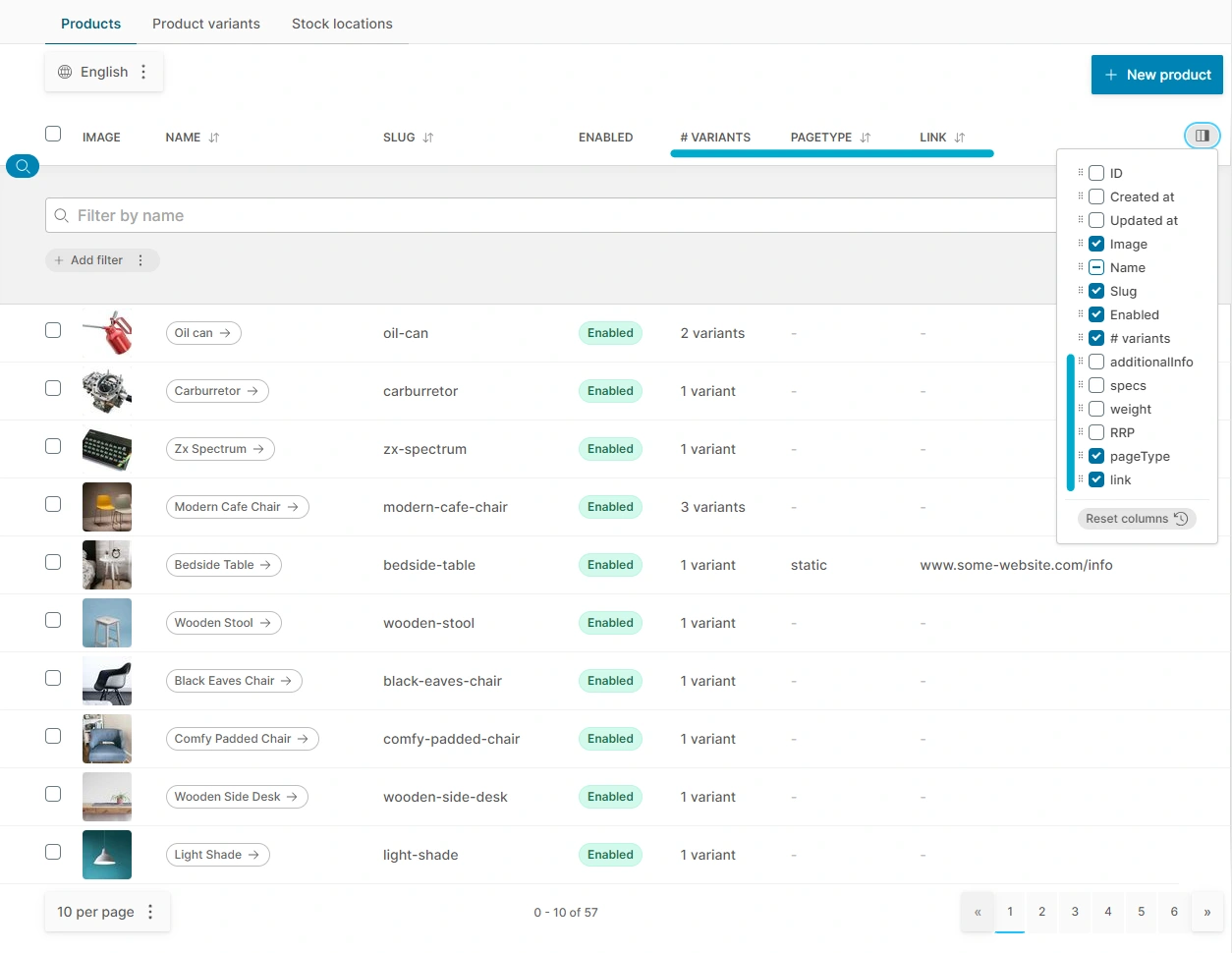
BIN
docs/content/developer-guide/customizing-models/custom-fields-data-table.webp
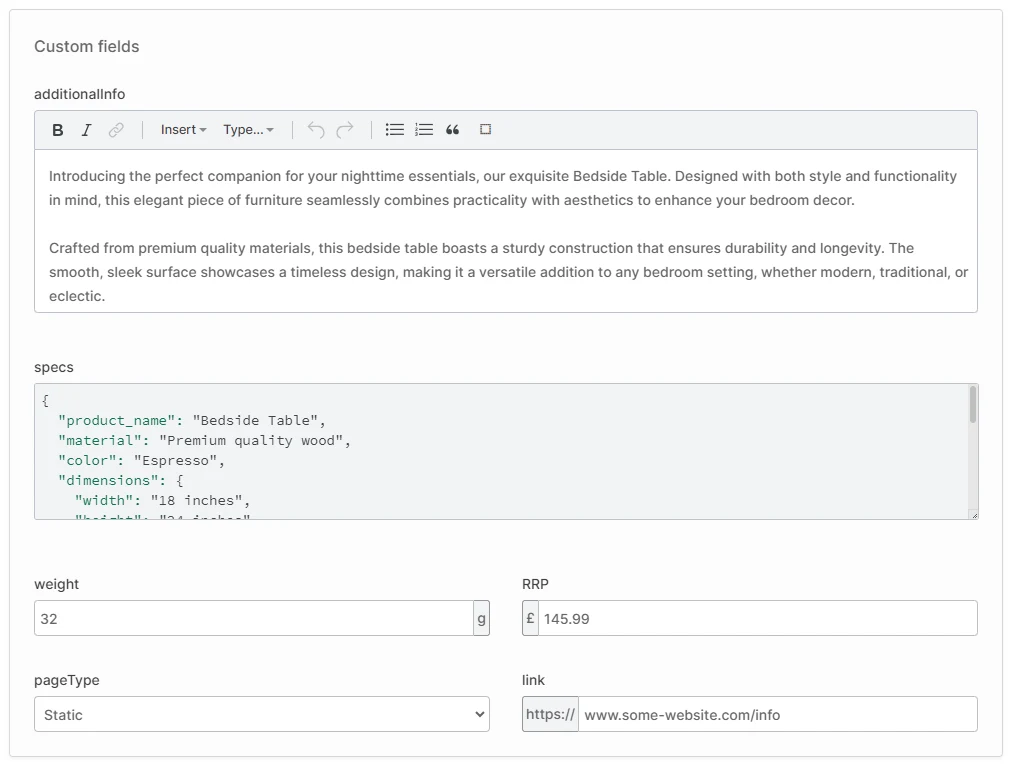
BIN
docs/content/developer-guide/customizing-models/custom-fields-ui.webp
+ 90
- 32
docs/content/developer-guide/customizing-models.md → docs/content/developer-guide/customizing-models/index.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
BIN
docs/content/developer-guide/customizing-the-order-process/custom-order-ui.webp

BIN
docs/content/developer-guide/customizing-the-order-process/custom_order_ui.jpg

+ 5
- 3
docs/content/developer-guide/customizing-the-order-process/index.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 68
- 3
docs/content/developer-guide/logging.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
BIN
docs/content/developer-guide/multi-tenant/channel-selector.png

BIN
docs/content/developer-guide/multi-tenant/create-admin.png

BIN
docs/content/developer-guide/multi-tenant/create-channel.png

BIN
docs/content/developer-guide/multi-tenant/create-role.png

+ 0
- 91
docs/content/developer-guide/multi-tenant/index.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 1
- 1
docs/content/developer-guide/overview/_index.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 50
- 15
docs/content/developer-guide/payment-integrations/index.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
BIN
docs/content/developer-guide/stock-control/global-stock-control.jpg

BIN
docs/content/developer-guide/stock-control/global-stock-control.webp

+ 1
- 1
docs/content/developer-guide/stock-control/index.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 88
- 31
docs/content/developer-guide/testing.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 1
- 1
docs/content/migrating-from-v1/breaking-api-changes.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 3
- 3
docs/content/plugins/_index.md
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
BIN
docs/content/user-guide/catalog/screen-facet-add.webp

BIN
docs/content/user-guide/catalog/screen-facet-list.webp

BIN
docs/content/user-guide/catalog/screen-inventory.webp

BIN
docs/content/user-guide/customers/screen-customer-group.webp

BIN
docs/content/user-guide/localization/screen-ui-language.webp

BIN
docs/content/user-guide/orders/screen-fulfillment-shipped.webp

BIN
docs/content/user-guide/orders/screen-fulfillment.webp

BIN
docs/content/user-guide/orders/screen-modification.webp

BIN
docs/content/user-guide/orders/screen-modify-button.webp

BIN
docs/content/user-guide/orders/screen-refund-button.webp

BIN
docs/content/user-guide/orders/screen-settle-payment.webp

BIN
docs/content/user-guide/settings/screen-shipping-test.webp

BIN
docs/content/user-guide/settings/screen-translations.webp

+ 2
- 2
docs/layouts/partials/top-bar.html
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 4
- 4
docs/layouts/shortcodes/alert.html
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
+ 7
- 1
packages/core/src/config/order/default-order-process.ts
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||