|
|
2 ani în urmă | |
|---|---|---|
| .devops | 2 ani în urmă | |
| .github | 2 ani în urmă | |
| examples | 2 ani în urmă | |
| media | 2 ani în urmă | |
| models | 2 ani în urmă | |
| pocs | 2 ani în urmă | |
| prompts | 2 ani în urmă | |
| scripts | 2 ani în urmă | |
| spm-headers | 2 ani în urmă | |
| tests | 2 ani în urmă | |
| .dockerignore | 2 ani în urmă | |
| .ecrc | 2 ani în urmă | |
| .editorconfig | 2 ani în urmă | |
| .gitignore | 2 ani în urmă | |
| CMakeLists.txt | 2 ani în urmă | |
| LICENSE | 2 ani în urmă | |
| Makefile | 2 ani în urmă | |
| Package.swift | 2 ani în urmă | |
| README.md | 2 ani în urmă | |
| SHA256SUMS | 2 ani în urmă | |
| build.zig | 2 ani în urmă | |
| convert-lora-to-ggml.py | 2 ani în urmă | |
| convert-pth-to-ggml.py | 2 ani în urmă | |
| convert.py | 2 ani în urmă | |
| flake.lock | 2 ani în urmă | |
| flake.nix | 2 ani în urmă | |
| ggml-cuda.cu | 2 ani în urmă | |
| ggml-cuda.h | 2 ani în urmă | |
| ggml-opencl.c | 2 ani în urmă | |
| ggml-opencl.h | 2 ani în urmă | |
| ggml.c | 2 ani în urmă | |
| ggml.h | 2 ani în urmă | |
| llama-util.h | 2 ani în urmă | |
| llama.cpp | 2 ani în urmă | |
| llama.h | 2 ani în urmă | |
| requirements.txt | 2 ani în urmă |
README.md
llama.cpp
Inference of LLaMA model in pure C/C++
Hot topics:
Description
The main goal of llama.cpp is to run the LLaMA model using 4-bit integer quantization on a MacBook
- Plain C/C++ implementation without dependencies
- Apple silicon first-class citizen - optimized via ARM NEON and Accelerate framework
- AVX2 support for x86 architectures
- Mixed F16 / F32 precision
- 4-bit integer quantization support
- Runs on the CPU
The original implementation of llama.cpp was hacked in an evening.
Since then, the project has improved significantly thanks to many contributions. This project is for educational purposes and serves
as the main playground for developing new features for the ggml library.
Supported platforms:
- [X] Mac OS
- [X] Linux
- [X] Windows (via CMake)
- [X] Docker
Supported models:
- [X] LLaMA 🦙
- [X] Alpaca
- [X] GPT4All
- [X] Chinese LLaMA / Alpaca
- [X] Vigogne (French)
- [X] Vicuna
- [X] Koala
- [X] OpenBuddy 🐶 (Multilingual)
Bindings:
- Python: abetlen/llama-cpp-python
- Go: go-skynet/go-llama.cpp
- Node.js: hlhr202/llama-node
- Ruby: yoshoku/llama_cpp.rb
UI:
Here is a typical run using LLaMA-7B:
make -j && ./main -m ./models/7B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin -p "Building a website can be done in 10 simple steps:" -n 512
I llama.cpp build info:
I UNAME_S: Darwin
I UNAME_P: arm
I UNAME_M: arm64
I CFLAGS: -I. -O3 -DNDEBUG -std=c11 -fPIC -pthread -DGGML_USE_ACCELERATE
I CXXFLAGS: -I. -I./examples -O3 -DNDEBUG -std=c++11 -fPIC -pthread
I LDFLAGS: -framework Accelerate
I CC: Apple clang version 14.0.0 (clang-1400.0.29.202)
I CXX: Apple clang version 14.0.0 (clang-1400.0.29.202)
make: Nothing to be done for `default'.
main: seed = 1678486056
llama_model_load: loading model from './models/7B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin' - please wait ...
llama_model_load: n_vocab = 32000
llama_model_load: n_ctx = 512
llama_model_load: n_embd = 4096
llama_model_load: n_mult = 256
llama_model_load: n_head = 32
llama_model_load: n_layer = 32
llama_model_load: n_rot = 128
llama_model_load: f16 = 2
llama_model_load: n_ff = 11008
llama_model_load: ggml ctx size = 4529.34 MB
llama_model_load: memory_size = 512.00 MB, n_mem = 16384
llama_model_load: .................................... done
llama_model_load: model size = 4017.27 MB / num tensors = 291
main: prompt: 'Building a website can be done in 10 simple steps:'
main: number of tokens in prompt = 15
1 -> ''
8893 -> 'Build'
292 -> 'ing'
263 -> ' a'
4700 -> ' website'
508 -> ' can'
367 -> ' be'
2309 -> ' done'
297 -> ' in'
29871 -> ' '
29896 -> '1'
29900 -> '0'
2560 -> ' simple'
6576 -> ' steps'
29901 -> ':'
sampling parameters: temp = 0.800000, top_k = 40, top_p = 0.950000
Building a website can be done in 10 simple steps:
1) Select a domain name and web hosting plan
2) Complete a sitemap
3) List your products
4) Write product descriptions
5) Create a user account
6) Build the template
7) Start building the website
8) Advertise the website
9) Provide email support
10) Submit the website to search engines
A website is a collection of web pages that are formatted with HTML. HTML is the code that defines what the website looks like and how it behaves.
The HTML code is formatted into a template or a format. Once this is done, it is displayed on the user's browser.
The web pages are stored in a web server. The web server is also called a host. When the website is accessed, it is retrieved from the server and displayed on the user's computer.
A website is known as a website when it is hosted. This means that it is displayed on a host. The host is usually a web server.
A website can be displayed on different browsers. The browsers are basically the software that renders the website on the user's screen.
A website can also be viewed on different devices such as desktops, tablets and smartphones.
Hence, to have a website displayed on a browser, the website must be hosted.
A domain name is an address of a website. It is the name of the website.
The website is known as a website when it is hosted. This means that it is displayed on a host. The host is usually a web server.
A website can be displayed on different browsers. The browsers are basically the software that renders the website on the user’s screen.
A website can also be viewed on different devices such as desktops, tablets and smartphones. Hence, to have a website displayed on a browser, the website must be hosted.
A domain name is an address of a website. It is the name of the website.
A website is an address of a website. It is a collection of web pages that are formatted with HTML. HTML is the code that defines what the website looks like and how it behaves.
The HTML code is formatted into a template or a format. Once this is done, it is displayed on the user’s browser.
A website is known as a website when it is hosted
main: mem per token = 14434244 bytes
main: load time = 1332.48 ms
main: sample time = 1081.40 ms
main: predict time = 31378.77 ms / 61.41 ms per token
main: total time = 34036.74 ms
And here is another demo of running both LLaMA-7B and whisper.cpp on a single M1 Pro MacBook:
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/1991296/224442907-7693d4be-acaa-4e01-8b4f-add84093ffff.mp4
Usage
Here are the steps for the LLaMA-7B model.
Get the Code
git clone https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp
cd llama.cpp
Build
In order to build llama.cpp you have three different options.
Using
make:On Linux or MacOS:
makeOn Windows:
- Download the latest fortran version of w64devkit.
- Extract
w64devkiton your pc. - Run
w64devkit.exe. - Use the
cdcommand to reach thellama.cppfolder. From here you can run:
make
Using
CMake:mkdir build cd build cmake .. cmake --build . --config ReleaseUsing
Zig:zig build -Drelease-fast
BLAS Build
Building the program with BLAS support may lead to some performance improvements in prompt processing using batch sizes higher than 32 (the default is 512). BLAS doesn't affect the normal generation performance. There are currently three different implementations of it:
- Accelerate Framework:
This is only available on Mac PCs and it's enabled by default. You can just build using the normal instructions.
- OpenBLAS:
This provides BLAS acceleration using only the CPU. Make sure to have OpenBLAS installed on your machine.
Using
make:On Linux:
make LLAMA_OPENBLAS=1Note: In order to build on Arch Linux with OpenBLAS support enabled you must edit the Makefile adding at the end of the line 105:
-lcblasOn Windows:
- Download the latest fortran version of w64devkit.
- Download the latest version of OpenBLAS for Windows.
- Extract
w64devkiton your pc. - From the OpenBLAS zip that you just downloaded copy
libopenblas.a, located inside thelibfolder, insidew64devkit\x86_64-w64-mingw32\lib. - From the same OpenBLAS zip copy the content of the
includefolder insidew64devkit\x86_64-w64-mingw32\include. - Run
w64devkit.exe. - Use the
cdcommand to reach thellama.cppfolder. From here you can run:
make LLAMA_OPENBLAS=1
Using
CMakeon Linux:mkdir build cd build cmake .. -DLLAMA_OPENBLAS=ON cmake --build . --config ReleasecuBLAS
This provides BLAS acceleration using the CUDA cores of your Nvidia GPU. Make sure to have the CUDA toolkit installed. You can download it from your Linux distro's package manager or from here: CUDA Toolkit.
Using
make:make LLAMA_CUBLAS=1Using
CMake:mkdir build cd build cmake .. -DLLAMA_CUBLAS=ON cmake --build . --config Release
Prepare Data & Run
# obtain the original LLaMA model weights and place them in ./models
ls ./models
65B 30B 13B 7B tokenizer_checklist.chk tokenizer.model
# install Python dependencies
python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt
# convert the 7B model to ggml FP16 format
python3 convert.py models/7B/
# quantize the model to 4-bits (using q4_0 method)
./quantize ./models/7B/ggml-model-f16.bin ./models/7B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin q4_0
# run the inference
./main -m ./models/7B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin -n 128
When running the larger models, make sure you have enough disk space to store all the intermediate files.
Memory/Disk Requirements
As the models are currently fully loaded into memory, you will need adequate disk space to save them and sufficient RAM to load them. At the moment, memory and disk requirements are the same.
| Model | Original size | Quantized size (4-bit) |
|---|---|---|
| 7B | 13 GB | 3.9 GB |
| 13B | 24 GB | 7.8 GB |
| 30B | 60 GB | 19.5 GB |
| 65B | 120 GB | 38.5 GB |
Quantization
Several quantization methods are supported. They differ in the resulting model disk size and inference speed.
| Model | Measure | F16 | Q4_0 | Q4_1 | Q4_2 | Q5_0 | Q5_1 | Q8_0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7B | perplexity | 5.9565 | 6.2103 | 6.1286 | 6.1698 | 6.0139 | 5.9934 | 5.9571 |
| 7B | file size | 13.0G | 4.0G | 4.8G | 4.0G | 4.4G | 4.8G | 7.1G |
| 7B | ms/tok @ 4th | 128 | 56 | 61 | 84 | 91 | 95 | 75 |
| 7B | ms/tok @ 8th | 128 | 47 | 55 | 48 | 53 | 59 | 75 |
| 7B | bits/weight | 16.0 | 5.0 | 6.0 | 5.0 | 5.5 | 6.0 | 9.0 |
| 13B | perplexity | 5.2455 | 5.3748 | 5.3471 | 5.3433 | 5.2768 | 5.2582 | 5.2458 |
| 13B | file size | 25.0G | 7.6G | 9.1G | 7.6G | 8.4G | 9.1G | 14G |
| 13B | ms/tok @ 4th | 239 | 104 | 113 | 160 | 176 | 185 | 141 |
| 13B | ms/tok @ 8th | 240 | 85 | 99 | 97 | 108 | 117 | 147 |
| 13B | bits/weight | 16.0 | 5.0 | 6.0 | 5.0 | 5.5 | 6.0 | 9.0 |
Interactive mode
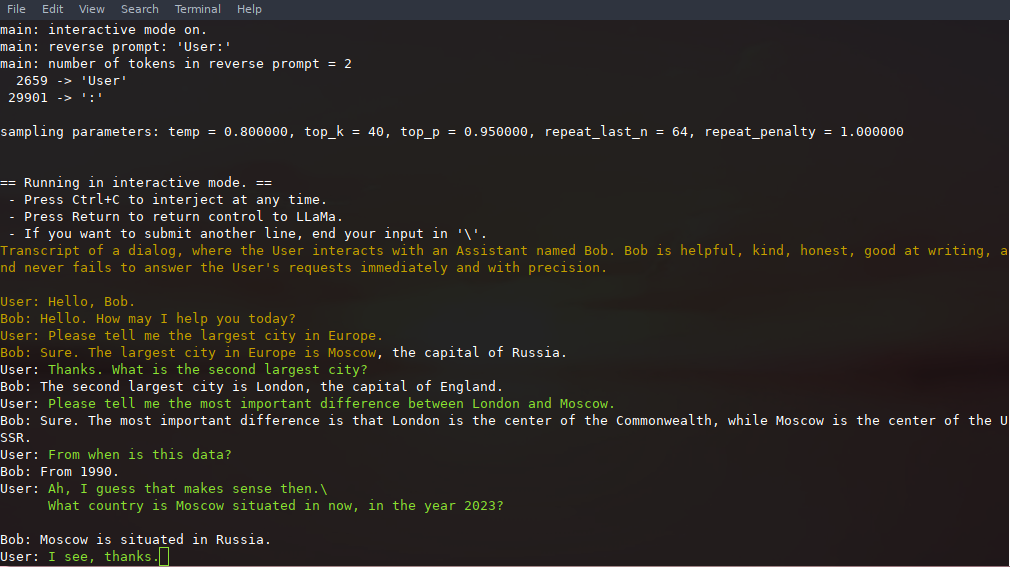
If you want a more ChatGPT-like experience, you can run in interactive mode by passing -i as a parameter.
In this mode, you can always interrupt generation by pressing Ctrl+C and entering one or more lines of text, which will be converted into tokens and appended to the current context. You can also specify a reverse prompt with the parameter -r "reverse prompt string". This will result in user input being prompted whenever the exact tokens of the reverse prompt string are encountered in the generation. A typical use is to use a prompt that makes LLaMa emulate a chat between multiple users, say Alice and Bob, and pass -r "Alice:".
Here is an example of a few-shot interaction, invoked with the command
# default arguments using a 7B model
./examples/chat.sh
# advanced chat with a 13B model
./examples/chat-13B.sh
# custom arguments using a 13B model
./main -m ./models/13B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin -n 256 --repeat_penalty 1.0 --color -i -r "User:" -f prompts/chat-with-bob.txt
Note the use of --color to distinguish between user input and generated text. Other parameters are explained in more detail in the README for the main example program.
Instruction mode with Alpaca
- First, download the
ggmlAlpaca model into the./modelsfolder Run the
maintool like this:./examples/alpaca.sh
Sample run:
== Running in interactive mode. ==
- Press Ctrl+C to interject at any time.
- Press Return to return control to LLaMa.
- If you want to submit another line, end your input in '\'.
Below is an instruction that describes a task. Write a response that appropriately completes the request.
> How many letters are there in the English alphabet?
There 26 letters in the English Alphabet
> What is the most common way of transportation in Amsterdam?
The majority (54%) are using public transit. This includes buses, trams and metros with over 100 lines throughout the city which make it very accessible for tourists to navigate around town as well as locals who commute by tram or metro on a daily basis
> List 5 words that start with "ca".
cadaver, cauliflower, cabbage (vegetable), catalpa (tree) and Cailleach.
>
Using GPT4All
- Obtain the
tokenizer.modelfile from LLaMA model and put it tomodels - Obtain the
added_tokens.jsonfile from Alpaca model and put it tomodels - Obtain the
gpt4all-lora-quantized.binfile from GPT4All model and put it tomodels/gpt4all-7B - It is distributed in the old
ggmlformat which is now obsoleted You have to convert it to the new format using
convert.py:python3 convert.py models/gpt4all-7B/gpt4all-lora-quantized.binYou can now use the newly generated
models/gpt4all-7B/ggml-model-q4_0.binmodel in exactly the same way as all other modelsThe newer GPT4All-J model is not yet supported!
Obtaining the Facebook LLaMA original model and Stanford Alpaca model data
- Under no circumstances should IPFS, magnet links, or any other links to model downloads be shared anywhere in this repository, including in issues, discussions, or pull requests. They will be immediately deleted.
- The LLaMA models are officially distributed by Facebook and will never be provided through this repository.
- Refer to Facebook's LLaMA repository if you need to request access to the model data.
Verifying the model files
Please verify the sha256 checksums of all downloaded model files to confirm that you have the correct model data files before creating an issue relating to your model files.
The following python script will verify if you have all possible latest files in your self-installed
./modelssubdirectory:# run the verification script python3 .\scripts\verify-checksum-models.pyOn linux or macOS it is also possible to run the following commands to verify if you have all possible latest files in your self-installed
./modelssubdirectory:- On Linux:
sha256sum --ignore-missing -c SHA256SUMS - on macOS:
shasum -a 256 --ignore-missing -c SHA256SUMS
- On Linux:
Seminal papers and background on the models
If your issue is with model generation quality, then please at least scan the following links and papers to understand the limitations of LLaMA models. This is especially important when choosing an appropriate model size and appreciating both the significant and subtle differences between LLaMA models and ChatGPT:
- LLaMA:
- GPT-3
- GPT-3.5 / InstructGPT / ChatGPT:
Perplexity (measuring model quality)
You can use the perplexity example to measure perplexity over the given prompt. For more background, see https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/perplexity. However, in general, lower perplexity is better for LLMs.
Latest measurements
The latest perplexity scores for the various model sizes and quantizations are being tracked in discussion #406. llama.cpp is measuring very well compared to the baseline implementations. Quantization has a small negative impact on quality, but, as you can see, running
13B at q4_0 beats the 7B f16 model by a significant amount.
All measurements are done against the wikitext2 test dataset (https://paperswithcode.com/dataset/wikitext-2), with default options (512 length context). Note that changing the context length will have a significant impact on perplexity (longer context = better perplexity).
Perplexity - model options
5.5985 - 13B, q4_0
5.9565 - 7B, f16
6.3001 - 7B, q4_1
6.5949 - 7B, q4_0
6.5995 - 7B, q4_0, --memory_f16
How to run
- Download/extract: https://s3.amazonaws.com/research.metamind.io/wikitext/wikitext-2-raw-v1.zip?ref=salesforce-research
- Run
./perplexity -m models/7B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin -f wiki.test.raw Output:
perplexity : calculating perplexity over 655 chunks 24.43 seconds per pass - ETA 4.45 hours [1]4.5970,[2]5.1807,[3]6.0382,...And after 4.45 hours, you will have the final perplexity.
Android
You can easily run llama.cpp on Android device with termux.
First, obtain the Android NDK and then build with CMake:
$ mkdir build-android
$ cd build-android
$ export NDK=<your_ndk_directory>
$ cmake -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=$NDK/build/cmake/android.toolchain.cmake -DANDROID_ABI=arm64-v8a -DANDROID_PLATFORM=android-23 -DCMAKE_C_FLAGS=-march=armv8.4a+dotprod ..
$ make
Install termux on your device and run termux-setup-storage to get access to your SD card.
Finally, copy the llama binary and the model files to your device storage. Here is a demo of an interactive session running on Pixel 5 phone:
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/271616/225014776-1d567049-ad71-4ef2-b050-55b0b3b9274c.mp4
Docker
Prerequisites
- Docker must be installed and running on your system.
- Create a folder to store big models & intermediate files (ex. /llama/models)
Images
We have two Docker images available for this project:
ghcr.io/ggerganov/llama.cpp:full: This image includes both the main executable file and the tools to convert LLaMA models into ggml and convert into 4-bit quantization.ghcr.io/ggerganov/llama.cpp:light: This image only includes the main executable file.
Usage
The easiest way to download the models, convert them to ggml and optimize them is with the --all-in-one command which includes the full docker image.
Replace /path/to/models below with the actual path where you downloaded the models.
docker run -v /path/to/models:/models ghcr.io/ggerganov/llama.cpp:full --all-in-one "/models/" 7B
On completion, you are ready to play!
docker run -v /path/to/models:/models ghcr.io/ggerganov/llama.cpp:full --run -m /models/7B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin -p "Building a website can be done in 10 simple steps:" -n 512
or with a light image:
docker run -v /path/to/models:/models ghcr.io/ggerganov/llama.cpp:light -m /models/7B/ggml-model-q4_0.bin -p "Building a website can be done in 10 simple steps:" -n 512
Contributing
- Contributors can open PRs
- Collaborators can push to branches in the
llama.cpprepo and merge PRs into themasterbranch - Collaborators will be invited based on contributions
- Any help with managing issues and PRs is very appreciated!
- Make sure to read this: Inference at the edge
- A bit of backstory for those who are interested: Changelog podcast
Coding guidelines
- Avoid adding third-party dependencies, extra files, extra headers, etc.
- Always consider cross-compatibility with other operating systems and architectures
- Avoid fancy looking modern STL constructs, use basic
forloops, avoid templates, keep it simple - There are no strict rules for the code style, but try to follow the patterns in the code (indentation, spaces, etc.). Vertical alignment makes things more readable and easier to batch edit
- Clean-up any trailing whitespaces, use 4 spaces for indentation, brackets on the same line,
void * ptr,int & a - See good first issues for tasks suitable for first contributions